Network Security
With copious amounts of data online and growing number of cyberthreats, it is essential to secure the user data by building a secure and stable network. Network security includes the steps that can be taken to ensure the reliability and integrity of all data in a network. With Digital Risk Analyzer, you can get the following checks done to ensure that your network is secure and reliable.
DNSSEC Validation
Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC) is an extension of the Domain Name Server (DNS) protocol that allows DNS responses to be digitally signed and authenticated. It adds cryptographic signatures to the existing DNS records and helps the DNS resolver to verify authenticity of the responses. This can help in identifying fake DNS records created through cache poisoning or during man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks. Digital Risk Analyzer will check if DNSSEC is enabled for the domain, whether there is any breakage in the chain, and whether the DNS records like A, AAAA, SOA, NS, MX, and TXT are signed with a valid key.
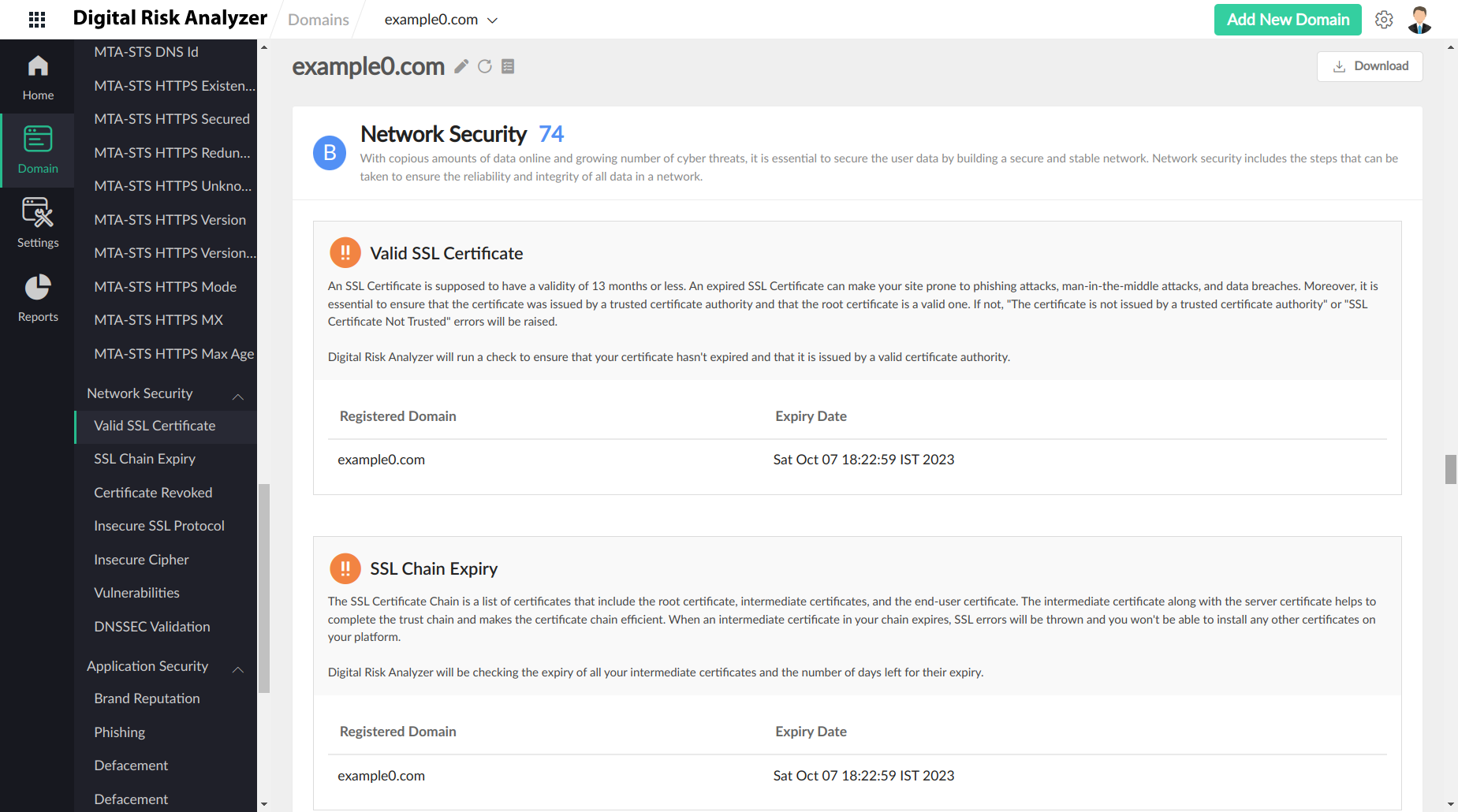
Valid SSL Certificate
An SSL Certificate is supposed to have a validity of 13 months or less. An expired SSL Certificate can make your site prone to phishing attacks, man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, and data breaches. Moreover, it is essential to ensure that the certificate was issued by a trusted certificate authority and the root certificate is a valid one. If not, "The certificate is not issued by a trusted certificate authority” or "SSL Certificate Not Trusted" errors will be thrown. Digital Risk Analyzer will run a check to ensure that your certificate hasn't expired and that it is issued by a valid certificate authority.
Insecure SSL Protocol
Using SSL protocols that aren't secure can make your site prone to data thefts, stealing, vulnerabilities, or other attacks. The presence of a secure protocol will hinder an attacker's attempt to tamper or modify sensitive data. Digital Risk Analyzer will verify the supported TLS protocol versions and will assess the level of security based on version hierarchy.
SSL Chain Expiry
The SSL Certificate Chain is a list of certificates that include the root certificate, intermediate certificates, and the end-user certificate. The intermediate certificate along with the server certificate helps to complete the trust chain and makes the certificate chain efficient. When an intermediate certificate in your chain expires, SSL errors will be thrown and you won't be able to install any other certificates on your platform. DigitalDomain Risk Analyzer will be checking the expiry of all your intermediate certificates and the number of days left for their expiry.
Certificate Revoked
A certificate is revoked when there are signs that the private key has been tampered with or is done immediately before the date of expiry as an act of invalidation. The revoked certificates will be stored in the Certificate Revocation List (CRL) managed by the certifying authority. It is not possible to check and verify that your certificates aren't there in the CRL. Hence, the easiest way to do that is using Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP). Digital Risk Analyzer will run OCSP checks to verify whether your certificates have been revoked or not.
SSL Certificate Vulnerabilities
SSL Certificate Vulnerabilities arise because of improper configuration of the SSL certificates. The most common vulnerabilities include BEAST, POODLE, POODLE (TLS), ROBOT, RC4 Vulnerability, CBC Vulnerability, AEAD, etc,. These vulnerability can lead to session hijackings, MITM attacks, text command injections, and many other security issues. Digital Risk Analyzer will check the SSL certificates to trace out any of the above mentioned vulnerabilities.
Insecure Cipher
A cipher is an algorithm for encryption and decryption of data. Ciphers enable private communication on different networking protocols, including the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol that offer encryption of network traffic. They use a system of fixed rules to transform plain text, or a message, into cipher text, a random string of characters. Your application or sever can be prone to vulnerabilities if you haven't configured any order for your ciphers, or if there are any insecure ciphers. The chances for an attacker to eavesdrop or tamper with your data is high if you have insecure ciphers. To avoid vulnerabilities, Digital Risk Analyzer will run a check to trace out weak ciphers with less than 128 bits, NULL ciphers, ciphers without encryption, etc.
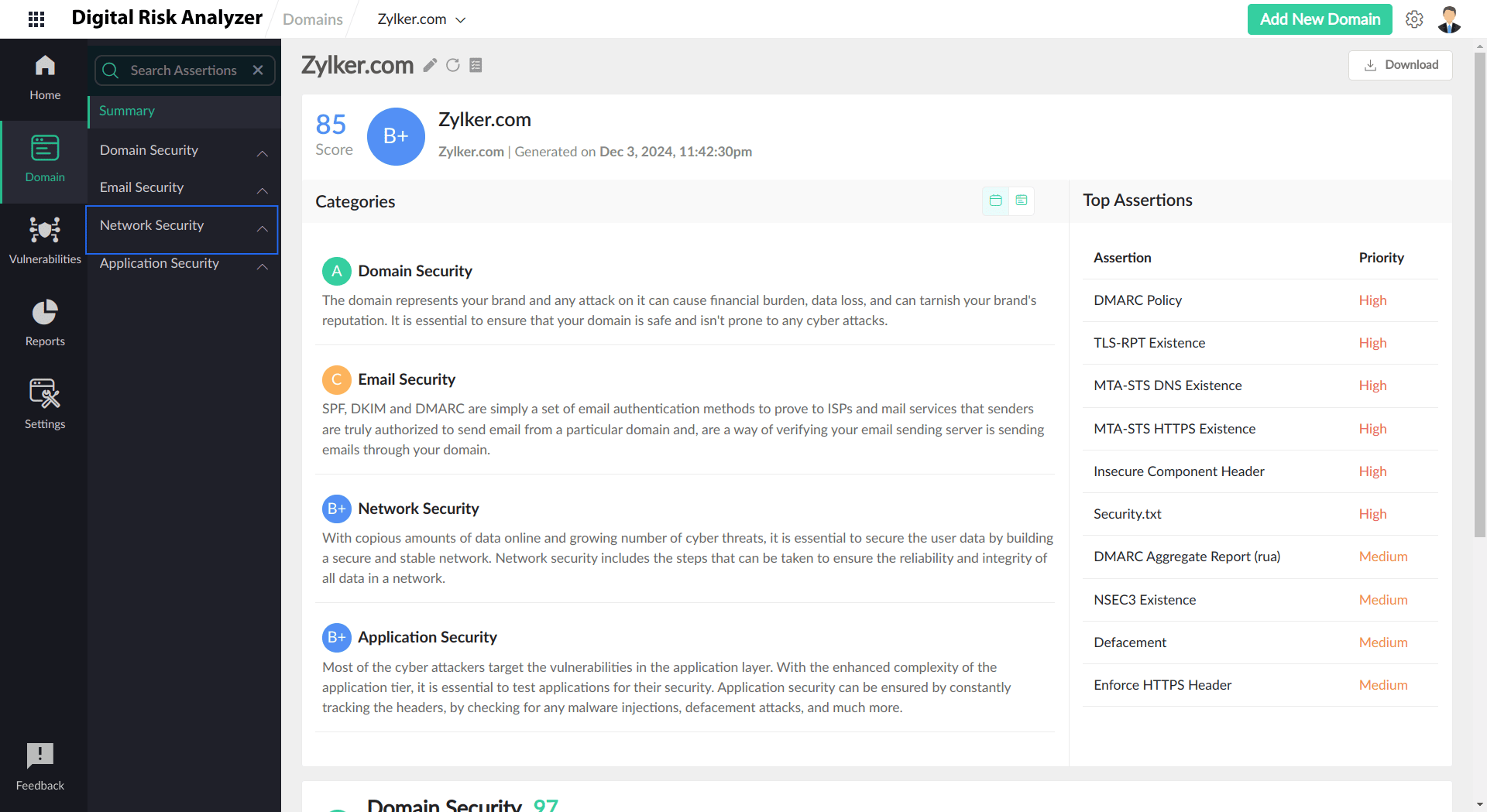
Open Ports
Get a consolidated report on your open ports, their severity, and associated details using Open Ports. Malicious attackers can exploit open ports in your server and gain unauthorized access to your system, leading to interception, manipulation, theft, and leakage of sensitive information. They can also install a backdoor and deploy ransomware to corrupt the entire system. Open Ports assertions help identify known and unknown open ports by scanning over 2,500 ports and warning you of possible threats they can cause.
View the Open Ports report by following the given steps:
- On the Report page, from the left pane, click Network Security.
- From the drop-down, select Open Ports.
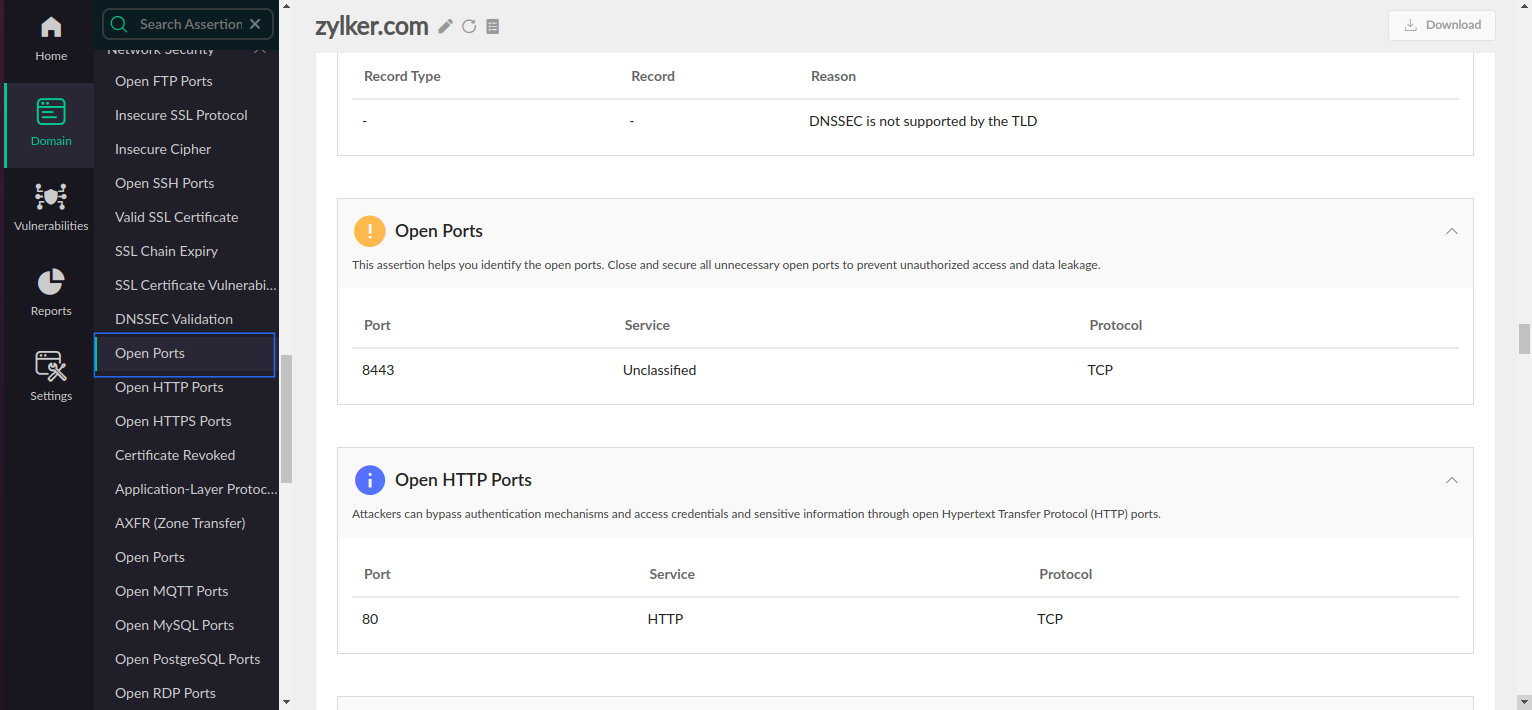
- From the list of scanned ports that are displayed, select the open ports to know their severity, risk, and associated details. Close ports based on severity level to mitigate potential threats from attackers.
